- 产品
- 公司
- 支持
- 产品
Ethernet Advanced Features for Automotive Applications
The roots of Ethernet technology began in 1973, when Bob Metcalfe, a researcher at Xerox Research Center (who later founded 3COM), wrote a memo entitled “Alto Ethernet,” which described how to connect computers over short-distance copper cable. With the explosion of PC-based Local Area Networks (LAN) in businesses and corporations in the 1980s, the growth of client/server LAN architectures continued, and Ethernet started to become the connectivity technology of choice for these networks. However, the Ethernet advancement that made it the most successful networking technology ever was when standardization efforts began for it under the IEEE 802.3 group.
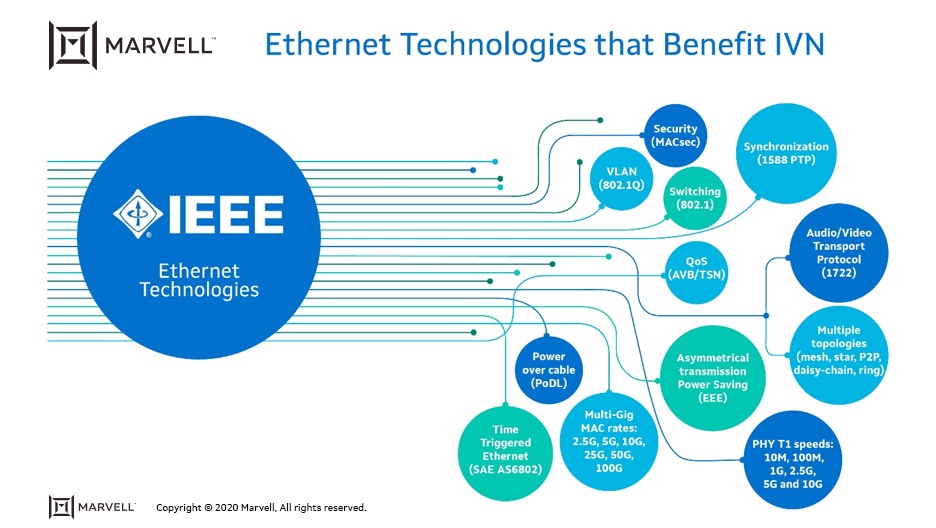
1) Switching
Addressing devices and switching through multiple routes provides redundancy that is critical for the functionality and reliability of the IVN. The switching architecture of the Ethernet LAN is based on the IEEE 802.1 standard. It defines the link security, overall network management, and the higher protocol layers above the Media Access Control (MAC).
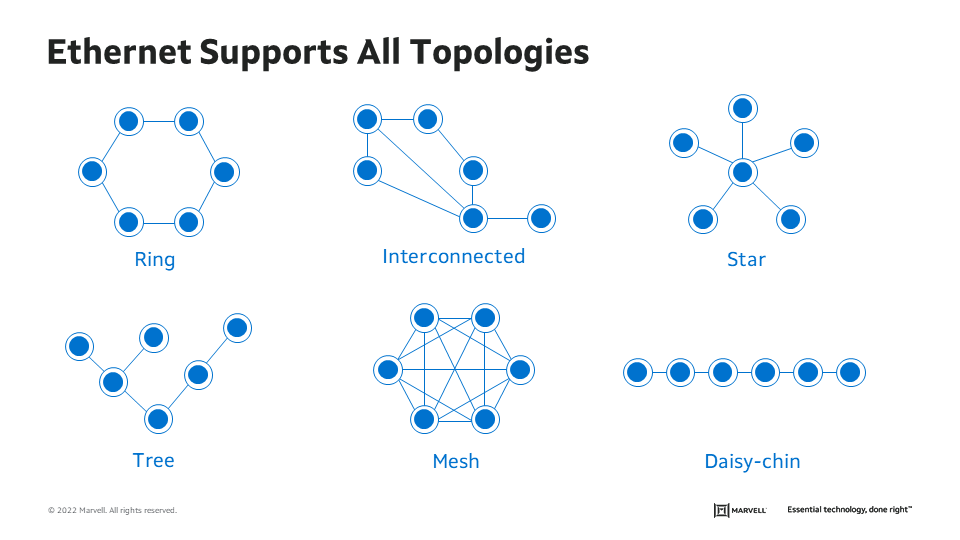
Figure 2
2) Ethernet PHY Speeds
Currently, Automotive Ethernet PHY standards are in progress for speeds higher than 10Gbps. The first effort to develop a pre-standard set of specifications is done in the NAV (Networking for Autonomous Vehicles) Alliance(www.nav-alliance.org), under Technical Working Group 1 (TWG1). In addition, a new task force, called IEEE 802.3cy for “Greater than 10 Gb/s Automotive Ethernet Electrical PHYs” began its activities in July 2020, with an objective to develop an automotive PHY for data rates of 25 Gbps, 50 Gbps and 100 Gbps.
3) Ethernet MAC speeds
4) Asymmetrical Ethernet
5) Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
6) Precision Time Protocol
7) Audio Video Bridging (AVB/TSN)
- A reservation protocol that enables the endpoint device to notify the various network elements to reserve resources necessary to support its stream.
- Queuing-and-forwarding defined rules to ensure that an AV stream will pass through the network within the delay specified in the reservation.
In November 2012, AVB was renamed “Time-Sensitive Networking Task Group” (TSN), which is an enhancement of AVB that added specifications to expand the range, functionality and applications of the standard.
IEEE 1722 – Layer 2 Audio/Video Transport Protocol (AVTP) for Time Sensitive Applications in a Bridged Local Area Network - sets the presentation time (time-stamping) for each AV stream and manages latencies.
The AVnu Alliance(www.avnu.org ) is an industry forum dedicated to the advancement of AV transport through the adoption of IEEE 802.1 AVB/TSN and the related IEEE 1722 standard. The Alliance is used by most OEM and Tier-1 companies to define a complete Ethernet-based solution for audio and video in IVNs.
8) MAC-PHY Security
MACSec is capable of identifying and preventing security threats, such as intrusion, man-in-the-middle, masquerading, passive wiretapping and playback attacks in the IVN.
9) Power Over Cable
In our next blog, we will discuss Ethernet QoS for IVN, the related standards and features, as well as the AvNU certification of Marvell Automotive Switch products.
标签: 1000BASE-T1, 100BASE-T1, 88Q2220 and 88Q2221, Audio video bridging, Automotive, Automotive Ethernet, Automotive Ethernet PHY, Automotive Switch, Autonomous drive, IEEE standard, In-vehicle networking, IVN, MACsec, Media Access Control, Security, TC10, VLAN
最近推文
档案文件
类别
- 5G (12)
- AI (10)
- 汽车 (26)
- Cloud (7)
- Coherent DSP (2)
- 公司动态(100)
- Custom Silicon Solutions (1)
- 数据中心(39)
- Data Processing Units (22)
- Enterprise (25)
- ESG (6)
- 以太网适配器和控制器(12)
- Ethernet PHYs (4)
- Ethernet Switching (30)
- Fibre Channel (10)
- 网络 (31)
- Optical Modules (8)
- Security (3)
- Server Connectivity (14)
- SSD Controllers (6)
- 存储 (22)
- Storage Accelerators (2)
- What Makes Marvell (12)